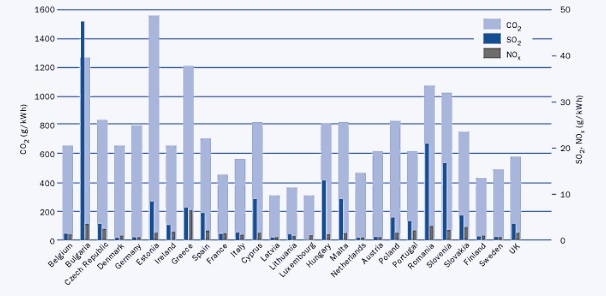
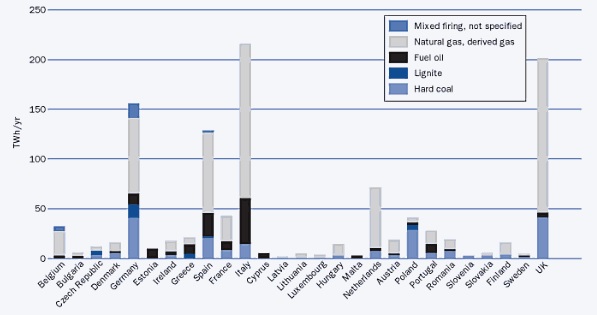
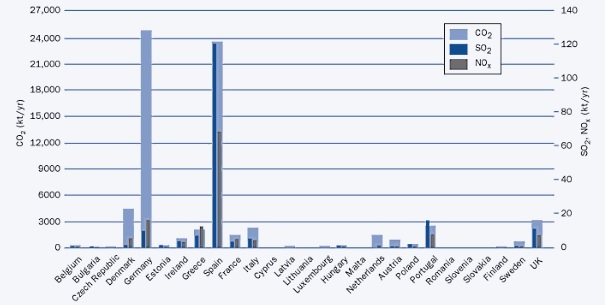
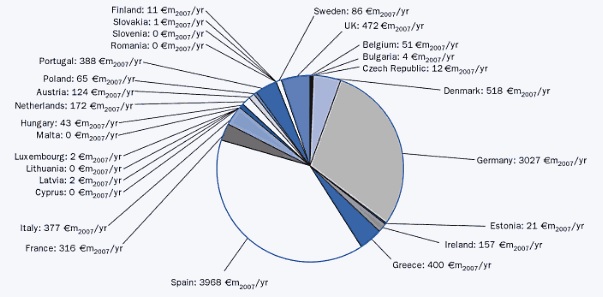
Summary
Pushing Hands is a film directed by Ang Lee that describes the life of an elderly Chinese man who lives with his grandson in America. The grandfather is a Beijing trainer who teaches martial arts and moves to New York, where his grandson and his wife live. The film reflects purely on the difference between Eastern culture’s conventional ideals and the sophisticated style of Western life. Conflicts emerge in the household as the patriarch returns to city life, which gives rise to discomfort in family relationships. The film illustrates the challenges facing the old man in modern life and the strategies he employs to respond to the violent wife of his grandson. Mr. Chu (Sihung Lung), his grandson Alex (Bo Z.Wang) and his wife Martha are the main characters in the film (Deb Snyder).
In this film, Lee discusses the cross-cultural relationships, tensions and problems associated with them. This film is a first of a kind where a father with a conventional history faces a shifting world of living. This film depicts a traditional Chinese man’s wisdom and warmth in a family with a full urban past. In this film, Alex’s character is also trapped between his traditional grandfather and his fussy, modern wife. For the grandson and grandfather, it is a painful circumstance, when they share blood relationships and have to keep up with the demands of each other. The film finally shows Mr. Chu regaining his grasp on life and moving on independently.

Plot of the Movie
The storey of the film is the life of Mr. Chu, an elderly and retired Chinese martial arts master, who travels to New York to join his grandson, Alex. Alex lives with Martha, an American woman who is his wife and is also a talented journalist. Martha is a neurotic who suffered from the block of the writer, which is a disorder that often affects the writer because of overwriting or lack of motivating thoughts. “As it so happens, Martha’s writer’s block started about the same time Mr. Chu moved in, and no one is more aware of this fact than she”As it happens, around the same moment Mr. Chu moved in, Martha’s writer’s block began, and no one is more aware of this fact than she. As Mr. Chu joined the Alex family, his wife was in a disturbed state, leaving Mr. Chu and Martha’s relationship sour.
As the movie “Pushing Hands” initiates, Mr. Chu is shown to be already in New York with his grandson and is uncomfortable and sharing a negative relationship with Martha. The film focuses much on this retired Chinese martial art teacher and his attempts to cope up with his new living atmosphere .In this he also attempts to teach Tai – Chi in a local school, where Alex is a student of Chinese Language. In the following part Mr.’ Chu encounters with a Chinese lady Mrs. Chen, and develops an attraction for her. However, due to Mr. Chu’s less aggressive nature this attraction towards Mrs. Chen s tends to falls out .Normally speaking, this movie tells all about the plight of an old Chinese immigrant in a foreign land and his attempts to fit in the new land of modernism.
Background and Theme of the Movie
The movie “Pushing Hands” is written by two writers namely; AngLee and James Schamas.Ang Lee is a Taiwanese man who made use of his Taiwanese heritage to create memorable movies which earned acclamation throughout the world. He has earned Masters from New York University on film, and got noticed in film arena with his classical movie like “The Wedding banquet”. This movie has earned him Academy award nomination and earned recognition as a director who crossed cultural and national barriers. James Shcamas is the co – writer of this movie “Pushing Hands” and also is an independent film producer and screen writer. During 1990s, James Schamus have produced many interesting films which gained much attention and appraisal from film fraternity. He is known for taking risks to bring about stories with is of challenging and versatile nature.
“The theme of the movie “Pushing Hands” is a clash of culture that is prominently seen between Mr. .Chu and the wife of his grandson. The film positions Mr. Chu, an elderly man, in a very dynamic urban arena in New York City and insists that he get used to it. The old man constantly copes with Martha, who is the wife of his grandson, along with New York City’s metropolitan lifestyle in the first half of the film. The film first sees him in a barren suburb of New York, coexisting with a daughter-in-law who is not of Asian descent and has almost no use for this lovely old man (Maslin). The film highlights on the complexities of the city life style and the point of views of an old man from a traditional Chinese background on this.
Movies in Parallel with Pushing Hands
The movie laid out for comparison and contrast with the movie “Pushing Hands” are “The Class” and “Brick lane”. The Movie “The Class” explains about the experience of a French teacher in dealing with the students in his class, who are of problematic nature. This film is based on a novel by Francois Bégaudeau ,and also stars him as a lead character in the movie, which is unique. The movie revolves completely in the school campus, and focuses on a teacher’s struggle to adjust with his rowdy type students and attempt to educate them. The character Marin as the tutor, fights daily with himself to educate the class which is highly disruptive .In the movie, even the smartest pupil called Esmeralda refuses to obey the tutor and in the climax the movie ends in utter violence.
The movie “Brick Lane” is all about the pathetic story of Bangladeshi women called Nazneen, who moved to London from rural area of Bangladesh upon marriage with a man much older to her. She was married to a man she completely dislikes and longed for a free life that her sister was leading back home in the village. She also bore two children from the dull marriage but was completely unsatisfied with the relationship with her husband. The movie takes a sharp turn when she falls in love with a handsome clothing worker who visits her house. The movie was set in the background of 9/11 period and showed the racial tensions and religious awareness existed in that duration.
Comparison of “Pushing Hands” with “The Class”
The Movie “Pushing Hands” is mainly about the life of an old martial art teacher from traditional background in an urban city called New York. Here the movie is concentrating on the ways in which old man called Mr.Chu trying to adjust with his Grandson’s family and their alien lifestyle in New York. He is trying hard to come in terms with the annoying and less friendly wife of Alex who is his grandson. Whereas in the movie “The Class”, the French tutor is as disturbed as Mr. Chu with his hostile students and trying all his luck to be friendly with them.” While the class has its share of diligent, well-behaved pupils like Asian immigrant Wei (Wei Huang), who speaks assuredly despite his less-than-perfect French, it’s the troublemakers who leave the most vivid impression”(Chang). We can here observe that both these movies depict the struggle of two people and steps they take to adjust to the difficult situation they are in.
Comparison of “Pushing Hands” with “Brick Lane”
In the movie “The Brick lane” the emphasis is on the Bangladeshi woman who moves to London city and the sorrow she go through in getting married to a man she never loved. She, same like Mr. Chu struggles to adjust with the city life and longs badly for her home country. Both the movie is increasingly expressing the way in which human sometimes have to live in conditions mostly they detest and have to fight against it. Even in both these movies, the key characters is in despair and falls in love with people for whom their desire in desperation. The movie explains that, at times it becomes difficult for people to live according to their will and has to surrender to the complexities and unfortunate situations in life.
Contrast of “Pushing Hands” with “The Class”
The movie “Pushing Hands” is a story of Chinese people and “The Class” is movie of French nationals. Here the key character is an elderly man and his interaction with his students who are teenagers. “If you’ve ever fought with a bunch of rowdy kids for control of a classroom, you know the tension that runs through the teaching sequences of The Class” (Jones). In the “Pushing Hands” the key character is struggling with one of his family members and is ending up in sorrow. Unlike the Key character Francois Bégaudeau, in movie “The Class” who is handsome and young, Mr. Chu is old and a retired person. In the movie “pushing Hands” Mr. Chu is a traditional Chinese man but in French movie the tutor Francois Bégaudeau is living in France and is modern and sophisticated.
Contrast of “Pushing Hands” with “Brick Lane”
In “Pushing Hands” the location is New York City which is part of America, while in “Brick lane” the movie is set in London city which is capital of United Kingdom. The story of “Pushing Hands” revolves around an old Chinese man and in “Brick Lane” the story is oriented on young Muslim women named Nankeen, who moves to London from a village of Bangladesh. According to (Durham)Nazneen plays the role with remarkable restraint, enduring a lifetime of dreams she could never live”The movie “Pushing hands” show the cultural clash and other movie show the young desires of a girl trapped in an unhappy relationship. Love and desire is a subject in “Brick Lane” whereas in the movie” Pushing Hands” survival of man in unconditional circumstances is highlighted.
The Important Message in the Movie ‘Pushing Hands”
The movie “Pushing Hands” reach out to people, in making them understand the difficulty an immigrant can face in a foreign land. In this Ang Lee tries to explain the cultural as well as relationship conflict that can occur in a family in the modern urban environment.Mr. Chu, the old man who moves with his grandson Alex, finds it extremely difficult to adjust with Alex’s wife Martha who is an American writer. In this movie, the Chinese gentleman Mr.Chu, who has been a martial art teacher throughout his life in China moves to New York to join his grandson and meets with solitude and despair. Here the director shows how urbanization has taken away the feeling of love and care from the minds of young generation.
In this movie, it is shown that a man from traditional background finds it very difficult to adjust with the technological and super advance life style of developed nation. The director also wants to let people know that men should try to hold on to circumstances, how much ever adverse they are. Life is not a ball game; it has twists and turns unexpected and young or old people need to confront it boldly. According to (Levy,45) “A gentleman, Mr. Chu has to face the cruel reality that, unlike the Chinese, Americans have no respect for the elderly”. This movie is a clear message to young generation that sophistication is something which has to be reflected in their morality and attitude in every society whether it is urban or rural.
Definition and Genrification of East Asian Cinema
East Asian Cinema can be defined as the film produced in East Asian region or by natives of East Asian countries. It can be referred to as a subsection of International cinema and includes all movies made by East Asian countries or natives. It includes mainly countries like China, Taiwan, Korea, Japan, Hong Kong. East Asian movies have a rich and diverse culture to project and this is the main reason for these films’ acclamation in foreign region. It is widely seen that Western countries have a high regard and obsessions for East Asian culture and heritage and this count for the success of these movies in West. The East Asian movies have an attribute of mystery, exotic quality and dangerous touch to it which other movies lack.
Normally East Asian movies represent Asian movies as a whole, and have immense recognition in UK and US and France. The East Asian cinema can be described as having the martial and heroical masculine genre. The violent action sequence of the East Asian movies has no equals in the cinema world. It is also evident that such aggressive masculine acts of violence have give way to a rise in homoerotic male bonding. The act of samurai from Japan, Tai- Chi and Kung fu from china, all were the important elements of East Asian movies which western audience yearn to see. Even though East Asian cinema covers a vast dimension of styles and genre, the, martial art and heroic masculinity is an all-time favorite of movie lovers all over the global.
Different Genres of East Asian Movies
The various genres of East Asian Movies can be classified as follows:
- a) Martial art movies: Martial art movies are very famous among all the genres of East Asian movies and it is also a symbolic style of East Asia. These fighting arts have such a charisma and elegance that it arouses anxiety and energy in western film world. The martial arts like kung fu , Taeakwondo and tai – chi all are of extremely potentiality for self-defense, and the same factor made it appealing to people all over the world.
- b) Samurai films: Samurai movies are more drama based than action movies. It has more violent and intense fighting and displays mentally and physically harmed warriors. The more exaggerated violent scenes in samurai films had an extraordinary substance to it, which made them special.
- c) Horror movies: The horror movies form East Asian genre can be classified to Japanese horror movies and Korean horror movies. Japanese horror movies are very focused on psychology and making the viewer look forward to and nervous. It also covers the subject of ghosts, possessions and exorcism with the occult in it. Korean dramas, on the other hand, rely more on character sufferings and hardships than supernatural powers.
- d) Japanese Animated Movies: It is a matter of surprise that the true roots of animation movies was in Japan. The date of origin of animated films can be traced back to 1916. For East Asian cinema, animated films such as Manga became a feather in the crown and received a great deal of popularity from worldwide audiences.
- e) Tokusatsu: These Japanese science fiction films are live action dramas that include special effects and super heroes. It has fantasy, horror and science fiction, which makes it a delight to watch as television series.
Japanese Directors of 1940- 1960 and Movies they Created in that Era
Some of the renowned directors of Japan during 1940 – 1960 can be listed as below:
1) Akira Kurosawa: He is a Japanese director who has made many movies during 1950s and 1960s which have crossed many conventional ideas of otherwise normal filmmaking. He is also a producer and screenwriter apart from being director. In 1990s, he was given life time achievement from academy awards jury. Some movies directed by him are Drunken Angel,Ikiru,Seven Samurai and Kagemusha.
2)Mikio Naruse: Mikio is a japanese movie director, producer and screen writer, who made more than 89 films in the duration of 1930 to 1967.His movies were dramatic, and focused on traditional and modern elements of Japanese culture. Few movies created by him were Travelling actors,A face from the past , Both you and I and Dancing girl.
3) Hayao Miyazaki: This Japanese film director was born in 1940, and has gained reputation as the world’ leading brain behind animated movies. He being the co – founder of Studio Ghibli, is the creator of movies like My neighbor Totoro, Princess Momonoke and Castle in the sky. As per, (Mcarthy,1945) Miyazaki is one of the few directors in the industry who personally check every key frame and redraws any he doesn’t find suitable a task most leave it to senior animators” One of his creation Spirited Aay is the highest grossing film of all time in Japanese film history.
Bibliography;
- Chang, Justin. “The Class.” www.variety.com. Reed Elsevier Inc., 23 May 2008. Web. 23 Apr 2011.
- Durham, Bryan. “Brick Lane – Movie Review.” www.mid-day.com. Mid-day Informedia Ltd., 29-05-2010. Web. 23 Apr 2011. <http://www.mid-day.com/entertainment/2010/may/290510-Brick-Lane-Movie-Review.htm>.
- Jones. “The Class: Powerful French classroom film.” www.cltampa.com. Creative Loafing Tampa, 2011. Web. 23 Apr 2011. <http://cltampa.com/tampa/the-class-powerful-french-classroom-film/Content?oid=2034381
- Levy, Emmanuel. Cinema of Outsiders: The Rise of American Independent Film. 1st ed., New York: New York University Press, 1999. 45. Print
- Maslin, Janet. “Pushing Hands (1992) FILM REVIEW;Another Wise, Gentle Patriarch.” www.movies.nytimes.com. The NewYork Times Company, 02-06-1995. Web. 23 Apr 2011. <http://movies.nytimes.com/movie/review?res=9B0CE1DC1639F931A35755C0A963958260>.
- Mcarthy, Helen. Hayao Miyazaki: master of Japanese animation: films, themes, artistry. 2nded.,. Berleley: Stone Bridge Press, 2002. 1945. Print
- Nix. “Pushing Hands (1992) Movie Review.” www.beyondhollywood.com/. Beyond Hollywood, 03-01-2005. Web. 23 Apr 2011. <http://www.beyondhollywood.com/pushing-hands-1992-movie-review/.>.